Object Navigation in AI2-THOR by SAVN
Ejection Fraction Measurement from Heart Ultrasound Images
Perception in Robotics Project
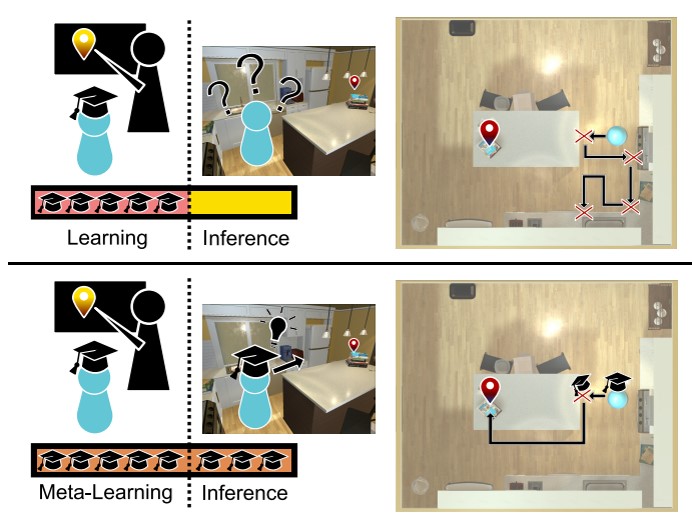
Object Navigation in AI2-THOR by SAVN
In this project, we demonstrate that the self-adaptive visual navigation (SAVN) model makes the agent conduct visual navigation successfully even when searching for unknown objects in unknown environments. Based on the meta-reinforcement learning architecture, such a model builds up the network to learn how to tune the weightings by itself. The result shows that SAVN outperforms the random-walking method both in success rate (SR) and success weighted by inverse path length (SPL). (video)
Machine Learning Project
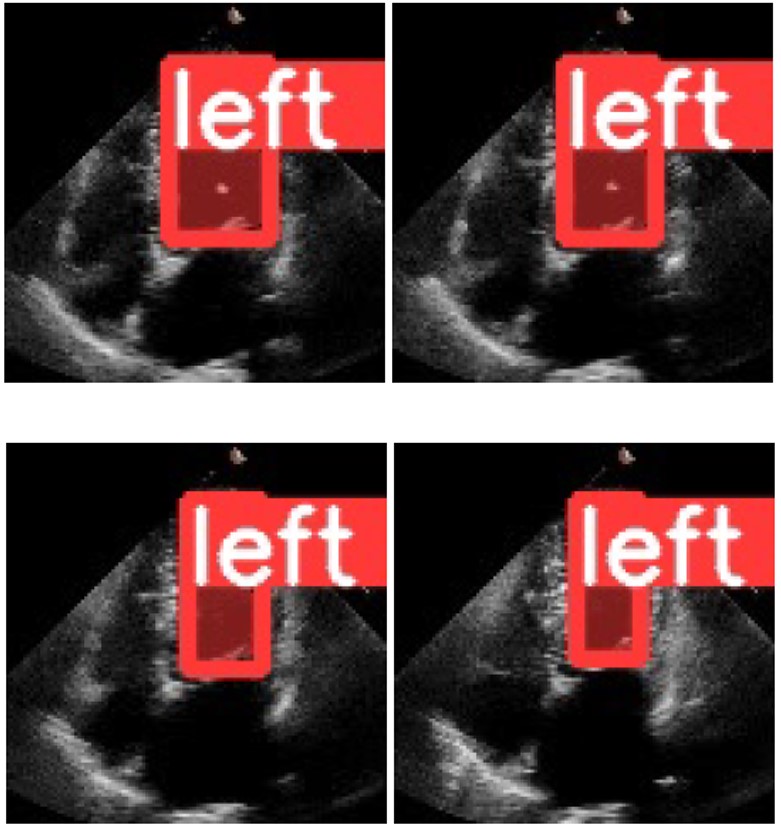
Ejection Fraction Measurement from Heart Ultrasound Images
This project aimed to detect the volume difference of the left ventricle during a cardiac cycle using YOLO-v7. Two datasets, HeartSeg and EchoNet-Dynamic, are transformed into the MS COCO dataset format, and the performance is tested. The results show that YOLO-v7 performs poorly on HeartSeg but well on EchoNet- Dynamic. However, detecting pixels of a target to compute the ejection fraction is found to be an unreliable method, as the standard deviation of the difference between the true value and prediction was significant, and the correlation value was minor. The reason for this is discussed, and a potential improvement method was provided. Additionally, an analysis of how YOLO-v7 works is also included. (video)
